Birth control pills, commonly known as "the pill," are daily oral contraceptives that contain hormones designed to prevent pregnancy. These hormones work by regulating the ovaries and uterus to prevent ovulation and create conditions that make pregnancy less likely. We offer a variety of birth control pills, providing effective and personalized birth control options to suit your needs.
Vendor:Omega
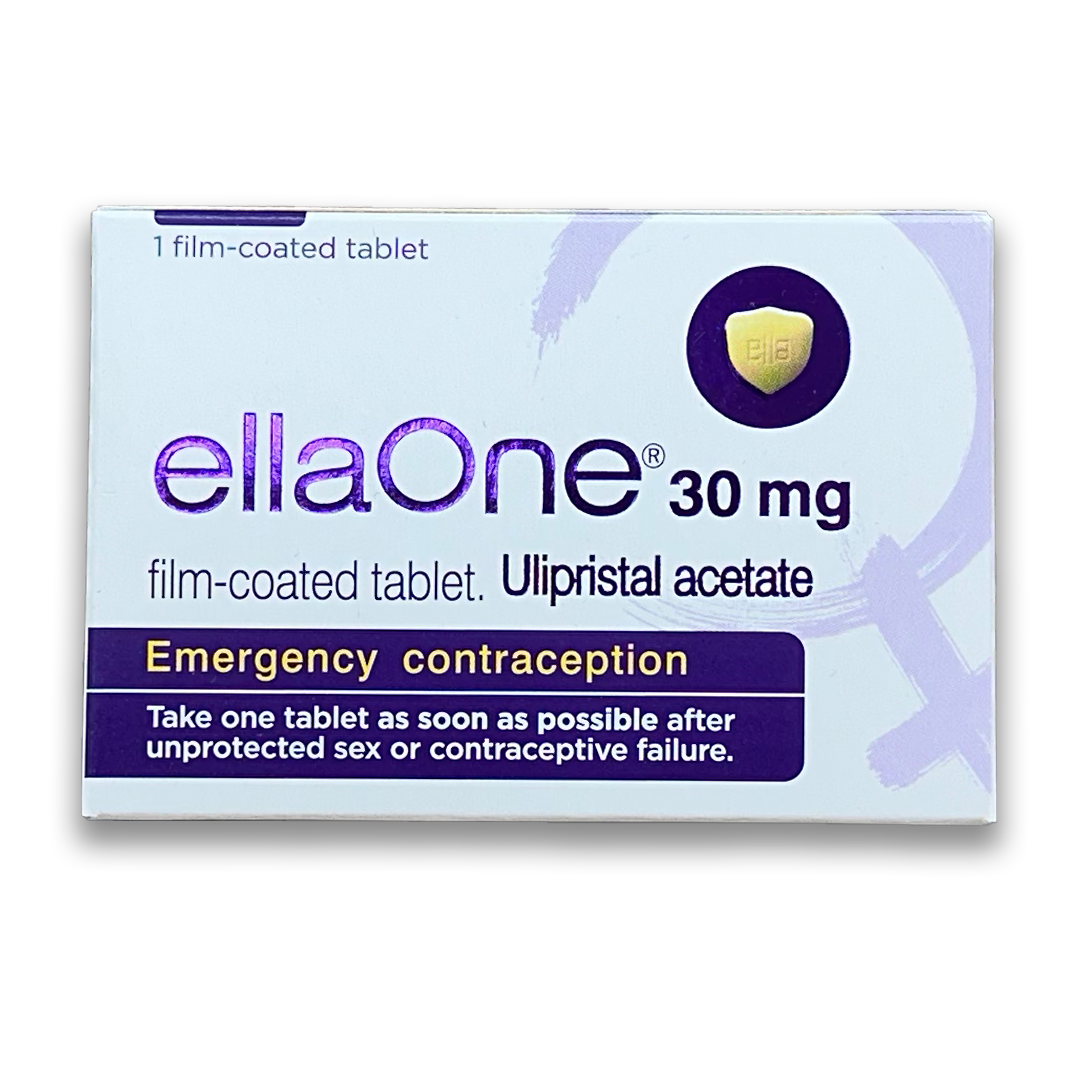
Ella One emergency contraceptive pills
180.00 SR
Vendor:ALLOGA MAXWELLIA
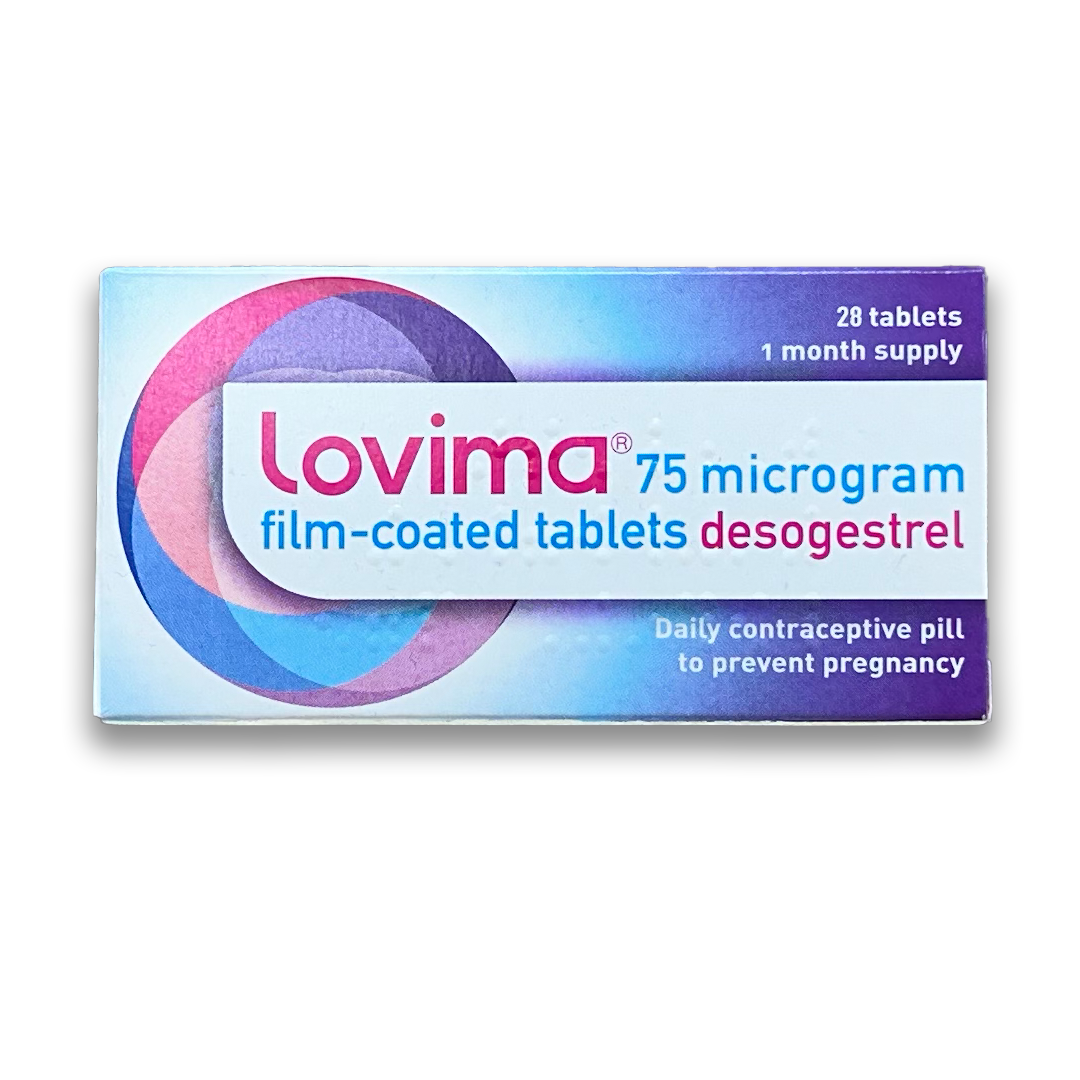
Luvima 75 microgram film-coated
59.94 SR
Vendor:Omega
Vendor:Organon
95.94 SR
Vendor:Bayer
165.00 SR
Vendor:Merck Sharp & Dohme Ltd
Cerazette 75 microgram tablets
107.94 SR
Vendor:Bayer
65.94 SR
Vendor:Bayer Plc
137.94 SR
Vendor:Pfizer
89.94 SR

About Contraceptives
Contraceptive methods
Who should use contraception?
Treatments
Why is contraception important?
More information
Frequently Asked Questions
Are contraceptives only for preventing pregnancy?
Can contraception protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs)?
Are there age restrictions for access to contraception?
Can I switch between different contraceptive methods?